What are the symptoms of bacterial infections?
Bacterial infections are caused by harmful bacteria entering the body and multiplying, leading to various symptoms that can range from mild to severe. Understanding the symptoms of bacterial infections is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This article delves into the common signs exhibited in adults, children, and infants, offering guidance on when it’s essential to seek medical attention.
Understanding Bacterial Infections: An Overview of Symptoms
Bacterial infections can manifest in a multitude of ways, depending on the type of bacteria involved and the individual’s immune response. Commonly, these infections may lead to inflammation, fever, and pain in the affected areas. Symptoms can vary widely; some individuals may exhibit mild signs, while others may experience severe and life-threatening issues. It’s important to differentiate between bacterial infections and viral infections, as the treatment methods vary significantly.
In many cases, bacterial infections can present as localized symptoms, such as redness, swelling, and pus formation, especially in skin infections. Systemic symptoms like fever, fatigue, and malaise can occur as the body mounts an immune response. For instance, a urinary tract infection may cause frequent urination and burning sensations, while pneumonia may lead to persistent cough and difficulty breathing.
A crucial aspect of recognizing bacterial infections is understanding that symptoms can evolve over time. Initially mild signs can escalate rapidly, necessitating vigilance and awareness. Maintaining a comprehensive understanding of these symptoms can facilitate early identification and prompt medical intervention, which is essential for effective treatment and recovery.
Common Symptoms of Bacterial Infections in Adults
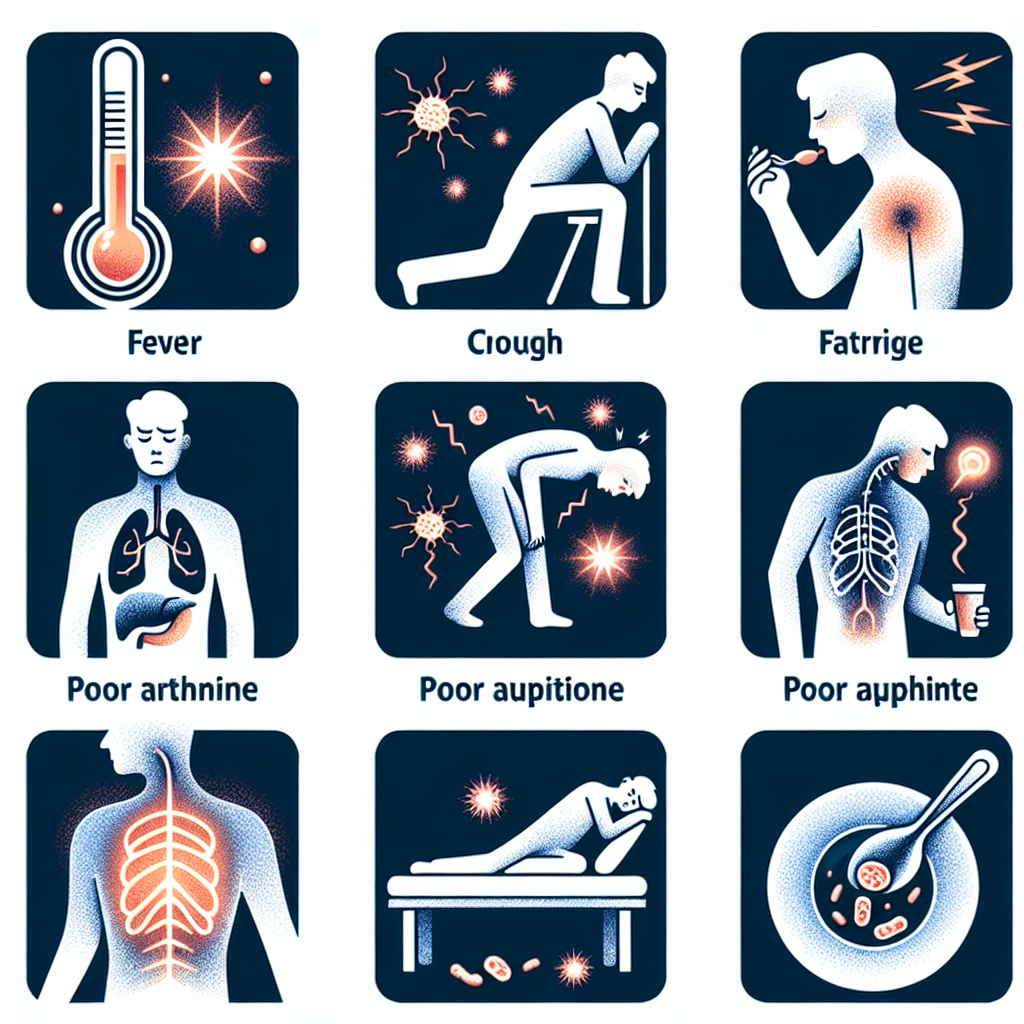
In adults, bacterial infections often present with well-known symptoms such as fever, chills, and fatigue. A fever is typically the body’s response to infection, signaling an underlying problem that may require medical evaluation. Along with fever, chills can cause discomfort and indicate the body’s struggle against the infection. Fatigue often accompanies these symptoms, as the immune system diverts energy to fight off the invading bacteria.
Localized symptoms are also common in adults. For instance, a skin infection may manifest as redness, warmth, and swelling in the affected area. In cases of respiratory infections, symptoms like a persistent cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Other infections, such as bacterial gastroenteritis, can lead to diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting, which may result in dehydration if not managed properly.
Severe bacterial infections can lead to more serious complications such as sepsis, where the infection spreads throughout the body. Symptoms of sepsis include confusion, disorientation, rapid heartbeat, and low blood pressure, which require immediate medical attention. Recognizing these severe symptoms is essential for timely intervention, as delays can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
Recognizing Unique Symptoms in Children and Infants
Children and infants may exhibit different symptoms when suffering from bacterial infections compared to adults. For example, a high fever in a child may indicate a bacterial infection, particularly when accompanied by irritability or lethargy. Infants, on the other hand, may present with subtle changes in behavior, such as decreased feeding or unusual fussiness, which can be early signs of an underlying infection.
In addition to fever, other symptoms like a rash, difficulty breathing, or ear pain may be indicative of bacterial infections in children. For instance, ear infections are common in young children and may present with tugging at the ear, irritability, and fever. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial since children can deteriorate rapidly due to infections, and timely intervention can prevent serious complications.
Moreover, gastrointestinal symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain may indicate a bacterial infection in children and infants. Dehydration is a significant risk in this demographic, making it essential for caregivers to monitor their child’s intake and seek medical advice if symptoms persist or worsen. Awareness of these unique symptoms is key to ensuring prompt treatment and recovery in the pediatric population.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Bacterial Infections
Timely medical intervention is critical when dealing with bacterial infections to prevent complications and improve outcomes. Individuals should seek medical attention if they experience severe symptoms such as high fever, persistent vomiting, or rapid breathing, which could indicate a more serious infection requiring immediate care. Warning signs like confusion, persistent pain, or sudden changes in consciousness are also critical indicators that warrant urgent medical evaluation.
Children and infants require special attention due to their developing immune systems. Caregivers should consult a healthcare provider if a child has a fever lasting more than a couple of days, shows signs of dehydration, or exhibits unusual behavior. Infants under three months with any fever should be evaluated promptly due to the risk of severe infections.
In addition to these symptoms, individuals with underlying health conditions or weakened immune systems should be particularly vigilant. Even mild symptoms can escalate quickly in these populations, and proactive healthcare management can lead to better health outcomes. Early intervention not only aids in quicker recovery but also reduces the risk of complications associated with bacterial infections.
Understanding the symptoms of bacterial infections is vital for prompt diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing common signs in adults, children, and infants, individuals can determine the appropriate time to seek medical attention. Timely intervention can make a significant difference in recovery and help prevent serious complications associated with bacterial infections. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to specific symptoms and conditions. For more information, you can visit CDC, Mayo Clinic, or World Health Organization.
Top hand sanitizers for virus protectionSeasonal flu vaccine effectivenessLatest research on virus transmissionRelevant LinkRelevant LinkRelevant Link